You may know that Forbes published tons of different and interesting lists, one of them is The World’s Billionaires. I took a look at the data and deepened my R knowledge alongside.
Countries
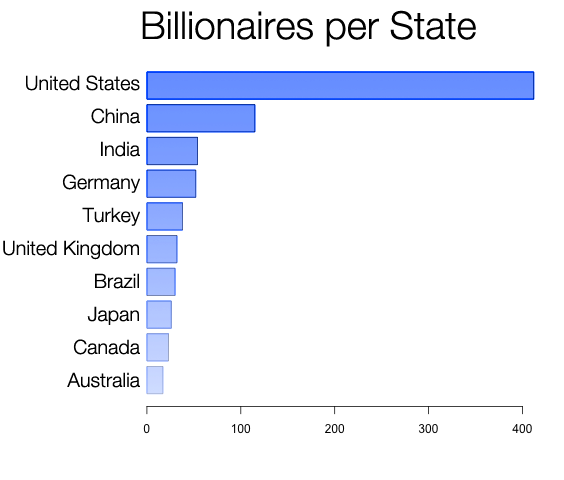
Let’s start with the countries. There are 1007 persons in this data set with valid Country entries.
You can see that most billionaires are born in the US and then with a big gap in China, India, Germany and Turkey. The relative distribution of billionaires worldwide looks a big different:
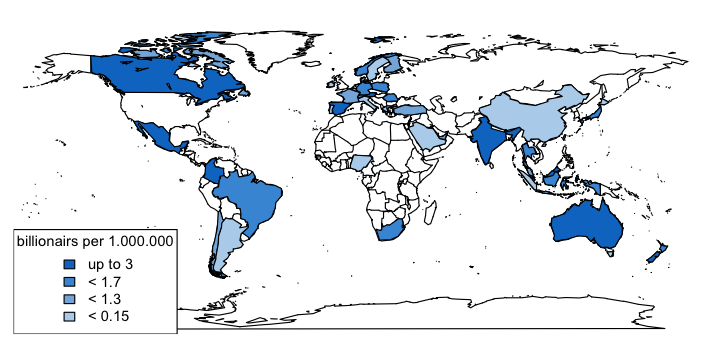
It mostly took some time to become a billionaire therefore I expect China and probably India to become stronger in the future.
Age
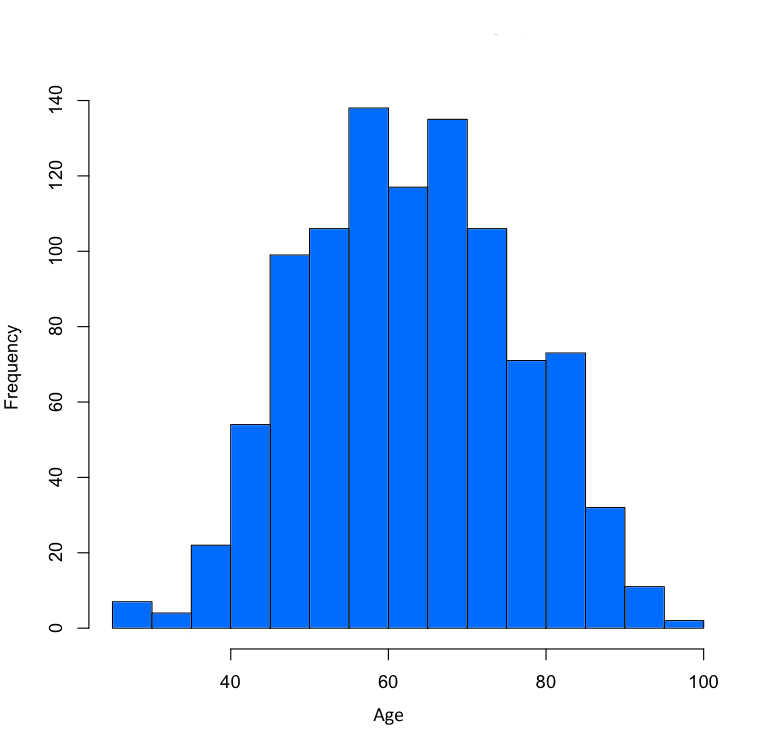
There are a few famous young billionaires like Mark Zuckerberg but most of them are quite older. The first quartile actually starts at 54, the average billionaire is 63 and the oldest one in this data set is 100.
Education
Only 51% of these people got at least a bachelor degree, 20% has a master degree and only 8.7% earned a doctorate or PhD.
Interestingly, about 5% are drop outs and 40 of these 50 drop outs are from the US.
Martial Status
Marriage is still high for billionaires. About 83% are Married, only 7% are divorced. About 5% are widowed and there are 30 singles.
Children
Children are also rather numerous. There are 176 entries with no data, i.e. either missing or no children.
Most billionaires got either two or three children but there are some outlines with 10 children or more. And there is Sulaiman Al Rajhi who got 23 children.
Net Worth
Most billionaires own between between 1 and 3.6 billion USD. The median billionaire owns 2.1 USD. There are, of course, some famous outlines like Bill Gates, Warren Buffett, Larry Ellison and Carlos Slim Helu. The complete net worth of all these billionaires is just 3.7 trillion USD. For comparison, the total US Debt is 14 trillion, that is nearly four times as much.
Self Made?
This was for me, one of the most interesting questions. I asked myself if there are differences between inherited and self-made billionaires between countries.
I’ll pick some examples.
US 69% are self-made
China 96% are self-made
Germany Only 33% are self made
Generally Emerging/New Countries, more self made, what is expected, but US positive example for an older country.
Source
Let’s talk about the sources. Rather interesting is that industries like oil and software which sound really profitable are rather minor industries. I think that has three reasons.
investments realestate diversified retail banking
84 84 57 53 40
pharmaceuticals hedgefunds media hotels construction
29 28 20 19 18
mining oil telecom coal finance
18 18 14 12 12
leveragedbuyouts manufacturing software oil&gas insurance
12 11 11 10 9
Firstly, becoming a billionaire takes time. It would be great to look at the first time someone became a billionaire, I think that you would probably see clusters, e.g. manufacturing probably started around 1940 but now there are less manufacturing billionaires.
Secondly, some markets aren’t that big. The global real estate market is probably a lot bigger than the global software market.
Thirdly, the ability to oligopolize markets. Let’s take oil and real estate. Oil is pretty much a commodity and you can distribute it world wide without problems. Real estate is locally limited, you can’t take a building block and just put it somewhere else, this limits the market power of companies in this industry.
You can access the data.csv here.